As we step into 2025, the landscape of manufacturing is undergoing a profound transformation, fueled by the rapid advancements in 3D printing technology. What once started as a niche technology for prototyping is now a mainstream method of manufacturing, offering unparalleled flexibility, efficiency, and customization. Today, 3D printing—also known as additive manufacturing—is at the forefront of changing how products are designed, produced, and delivered. This article explores the significant impact of 3D printing on manufacturing techniques, the key innovations driving its rise, and how it is revolutionizing various industries.
The Impact of 3D Printing on Manufacturing Techniques in 2025
In 2025, 3D printing has become an essential component of modern manufacturing processes, providing advantages over traditional methods that have long been in place. From more efficient design to on-demand production, the benefits of additive manufacturing have reshaped the industry and expanded its potential across various sectors.
Streamlining Production with Additive Manufacturing
Traditional manufacturing techniques, such as machining and injection molding, often involve complex steps, including tooling, material cutting, and assembly. These processes can be time-consuming, expensive, and produce significant material waste. On the other hand, 3D printing allows manufacturers to create objects layer by layer directly from a digital model, bypassing many of the time-consuming processes of traditional methods.
This layer-by-layer approach eliminates the need for physical molds or tooling, significantly reducing lead times and costs. Manufacturers can print products in one continuous process, drastically improving production efficiency. Additionally, the speed at which 3D printing can create parts means that businesses can better respond to market demands or adapt designs without extensive downtime. These capabilities enable companies to produce prototypes quickly, test designs in real-time, and make iterative improvements, which makes the entire manufacturing process more agile.
Mass Customization
One of the standout features of 3D printing is its ability to facilitate mass customization. While traditional manufacturing methods often require new molds or retooling for each unique design, 3D printing allows manufacturers to modify existing designs and produce personalized products with minimal changes to production lines.
For example, in industries like aerospace, automotive, and healthcare, mass customization plays a vital role. Companies can now design parts that are tailored to individual specifications, such as patient-specific medical implants, custom car parts, or lightweight aerospace components. By leveraging the flexibility of 3D printing, manufacturers can meet the growing demand for personalized solutions and provide customers with exactly what they need, without the costs associated with traditional manufacturing.
The ability to produce personalized products also improves the overall customer experience. By offering tailored solutions, companies can foster stronger relationships with their customers, creating a sense of uniqueness that mass production cannot provide.
Reducing Material Waste
Another critical advantage of 3D printing is its ability to reduce material waste. In traditional subtractive manufacturing processes, such as milling or machining, raw material is often cut away and discarded. This process leads to significant waste, both in terms of material and energy. In contrast, 3D printing builds objects layer by layer, using only the material needed for the final product.
This not only reduces the environmental impact of manufacturing but also lowers costs for businesses. By minimizing material waste, companies can make more efficient use of their resources and operate more sustainably. Moreover, the ability to recycle excess material in some 3D printing processes further supports sustainability goals, making it a key factor in reducing the overall ecological footprint of manufacturing.
Key Innovations Driving 3D Printing in the Manufacturing Sector
The rapid growth of 3D printing in manufacturing is driven by several key innovations in materials, technology, and production models. These developments are enhancing the capabilities of 3D printing and opening up new possibilities for its applications.
Advanced 3D Printing Materials
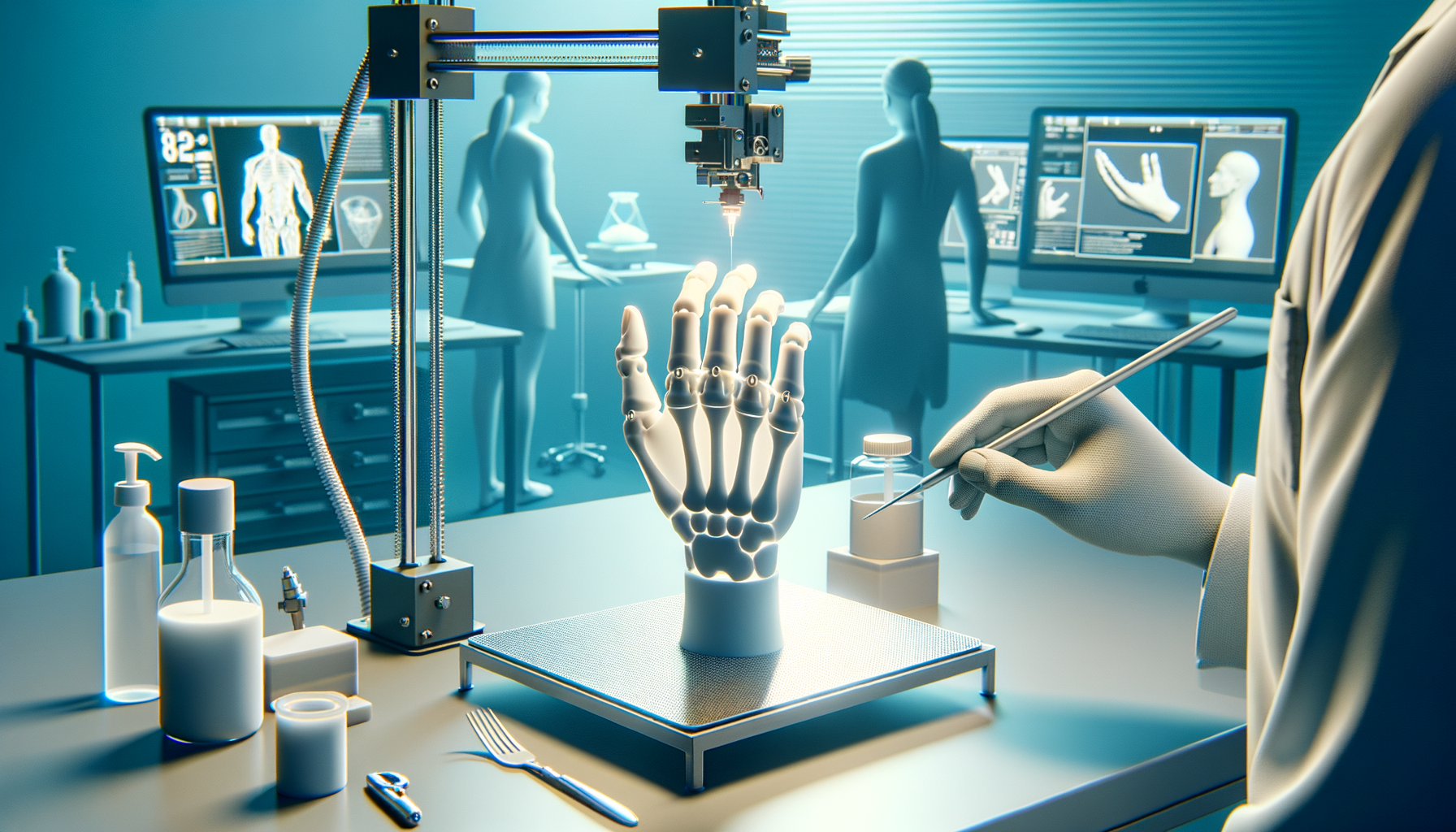
The development of new materials has been one of the most significant factors behind the growing adoption of 3D printing in manufacturing. In 2025, manufacturers have access to an expanded range of materials, including high-performance polymers, metal alloys, and biocompatible substances. These advanced materials have broadened the range of products that can be manufactured with 3D printing, allowing industries to create everything from lightweight aerospace components to complex medical implants.
Materials such as carbon fiber composites and titanium alloys are now available for use in 3D printing, which means manufacturers can create parts that are stronger, lighter, and more durable than ever before. The versatility of these materials has allowed 3D printing to be integrated into industries that require high-performance components, such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare.
In addition, the development of biocompatible materials is paving the way for the creation of medical devices and implants that are customized to individual patients. These advancements in material science are expanding the possibilities of what can be achieved with 3D printing and making it an essential tool for the future of manufacturing.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into the 3D printing process is another game-changer for the manufacturing sector. AI and ML technologies allow manufacturers to optimize the design and production process by analyzing large datasets and predicting potential issues before they arise.
For example, AI-powered algorithms can help manufacturers design more efficient parts that require less material without compromising strength or functionality. Machine learning can also optimize the printing process itself by continuously monitoring the production process and adjusting settings to improve quality and efficiency.
Moreover, AI can assist in predictive maintenance, allowing manufacturers to anticipate potential machine failures before they occur. This reduces downtime, increases operational efficiency, and extends the life of 3D printing equipment.
Decentralized Manufacturing and Supply Chain Innovation
The rise of decentralized manufacturing is one of the most exciting developments in the 3D printing industry. Traditional supply chains often rely on global manufacturing facilities and long-distance transportation, which can lead to delays, higher costs, and vulnerability to disruptions. 3D printing is enabling businesses to adopt localized production models, allowing them to manufacture products closer to the end consumer.
In 2025, many companies are adopting this approach, enabling them to respond quickly to demand fluctuations and reduce transportation costs. Localized production also allows businesses to manufacture products on demand, which can help reduce inventory costs and provide customers with faster delivery times.
This shift towards decentralized manufacturing also supports the concept of on-demand production, which reduces the need for large-scale inventories and the environmental impact associated with mass production. By embracing 3D printing as a decentralized manufacturing solution, companies can operate more efficiently, sustainably, and flexibly.
The Future of 3D Printing in Manufacturing
Looking ahead, the future of 3D printing in manufacturing appears bright. With continuous advancements in materials, technologies, and production models, 3D printing is poised to further disrupt traditional manufacturing methods and redefine the way products are created.
Overcoming Limitations of Current Technology
While 3D printing has made significant strides in recent years, there are still some limitations to overcome. Speed, for example, is an ongoing challenge. Traditional manufacturing methods can produce parts at a faster rate than most 3D printing processes, particularly when high volumes of parts are required. However, as 3D printing technologies continue to evolve, new techniques such as multi-material printing, faster printing speeds, and greater automation are expected to address these issues.
Another challenge is the cost of industrial-scale 3D printing, particularly for high-performance materials and large-scale prints. However, as the technology becomes more widespread, it’s expected that economies of scale will drive down costs, making 3D printing more accessible to businesses of all sizes.
Expanding Applications Across Industries
The potential applications of 3D printing in manufacturing are virtually limitless. Industries such as aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and consumer goods are already benefiting from the technology, and other sectors are expected to follow suit. As the capabilities of 3D printing continue to improve, we can expect to see even more industries adopting the technology to streamline production, reduce costs, and improve product quality.
In particular, industries that require highly customized, low-volume, or complex parts will continue to be prime candidates for 3D printing adoption. From custom medical implants to intricate automotive parts, 3D printing offers solutions that traditional manufacturing methods simply cannot match.
Conclusion
As we enter 2025, 3D printing is revolutionizing the manufacturing industry by offering unprecedented flexibility, efficiency, and customization. The ability to streamline production, reduce material waste, and facilitate mass customization is changing the way products are designed and produced. Furthermore, advancements in materials, artificial intelligence, and decentralized manufacturing are driving the expansion of 3D printing’s capabilities and applications.
The future of manufacturing is being shaped by the continued evolution of 3D printing technology. As businesses embrace these innovations, they can expect to unlock new levels of efficiency, sustainability, and customer satisfaction. By harnessing the power of 3D printing, manufacturers are positioning themselves for success in a rapidly changing global economy.
Call to Action
Are you ready to embrace the future of manufacturing? Learn more about how 3D printing can revolutionize your business and stay ahead of the competition in 2025. Explore the latest trends and innovations in 3D printing today.